Biohacking the Genome - BDNF gene
- Jul 13, 2025
- 3 min read

The BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor) gene holds the molecular information of the BDNF peptide, a neurotrophin, which plays a crucial role in the development, maintenance, and plasticity of neurons in the brain. Variants in the BDNF gene, such as the Val66Met polymorphism, can influence neurological and psychological processes. It has been implicated in conditions like depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and dementia.
"Among the hundreds of polymorphisms in the BDNF gene, BDNF rs6265 (G196A or Val66Met) in exon XI within the prodomain region of BDNF is one of the most common and consequential." (Chiaruttini et al., 2009).
Dysfunction (low excretion of the peptide) by the BDNF gene variant influences an individual in the following significant ways:
Neuroplasticity: BDNF is involved in neuroplasticity, which is the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. Acupuncture for example, which is believed to promote neuroplasticity, and individuals with certain BDNF variants may experience different levels of effectiveness due to variations in their neuroplastic response.
Pain Perception: BDNF is also involved in pain modulation. Variants in the BDNF gene can affect how individuals perceive pain and respond to pain-relief treatments.
Mood and Anxiety: BDNF is linked to mood regulation and anxiety. Effectiveness of treatments and medications may vary depending on the individual's BDNF genotype.
Response to Stress: BDNF variants can influence how individuals respond to stress, which can affect the overall effectiveness of stress reduction efforts.
How can one make the BDNF gene more functional, which may also increase the effectiveness of other neurological and psychological treatments.
Oh, you guessed it, imaet to the rescue:
Epigenetically upregulating the function of the BDNF gene. How? By resonating with the BDNF frequency (and associated genes) in the Biofield panel or the Allergens panel.

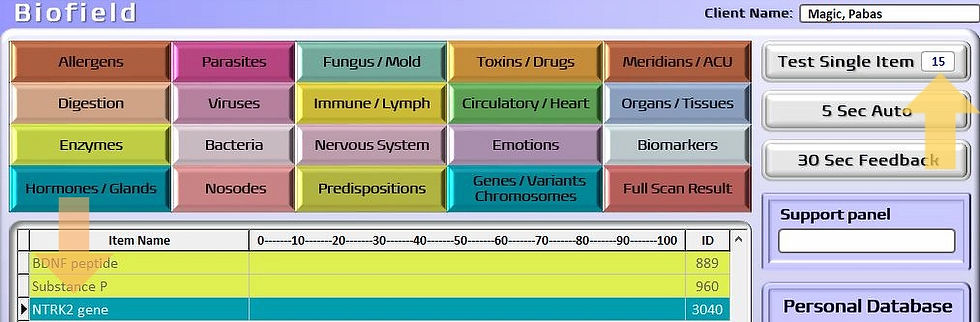
Test Single Item - the lower the number (1-100) the lower functioning the gene/enzyme. Any item below 40 is worthwhile considering to upregulate or to put into a feedback "basket".
BDNF peptide is listed under Enzymes, NTRK2 is under Genes/Variants/Chromosomes.
This can be done by search function and follow up with Test Single Item. Looking for low numbers.
OR, after a BioScan, the low functioning Genes will "automatically" list at the bottom of the Scan result. Chose a gene or enzyme from the bottom 30 of an Allergens BioScan result and transfer it into the feedback basket. Run a 15 - 20 minute feedback session. Always activate Quick Cycle.


There is a lot more to learn about gene behavior and how to beneficially influence gene expression epigenetically with the imaet technology. One can imprint frequencies on wearables. Generally speaking, you want to wear a frequency on and off, not constantly, depending on the type of gene you are working on.
For BDNF and trying to rehabilitate chronic stress damage, probably wearing it at nighttime is best and off during the day as the brain repairs itself mostly during sleep. Stay tuned, open minded and always be gentle with the body. We don't want to overpower the natural rhythm of things. One important rhythm in this regard is the organ clock. We want to work in harmony with the rhythms

of the body, the rhythms of nature and the rhythms of the universe.
PS: As of version 12.0, only the BDNF gene itself is in the imaet database. If it BioScans really low (or Single Item Test), one can assume that a SNP is present. Ultimately, it does not matter why BDNF is low functioning; simply the fact that it is low functioning is reason enough to resonate with it and epigenetically upregulate it.
Author: Dr Bernard Straile





Comments